Google Announces New AI-Based Search Updates
Last week, Google announced an array of useful new features to improve its search capability, leveraging a new(ish) AI-based approach that greatly enhances the way in which Google finds and displays answers to its search queries.
Sounds boring, right? Well, don’t put the kettle on just yet, because if you’re a marketer or a business owner, there are a couple of things you should take into consideration when you’re reviewing your SEO. There’s a few quirky new features too, so let’s take a look at what makes this new system tick.
So What’s The Deal?
On the face of it, the change seems merely a product of Google’s continued mission to make search easier and faster for users. In his blog, Google’s Head of Search Prabhakar Raghavan describes how they are:
“…bringing the most advanced AI into our products to further our mission to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
The AI in question, known as BERT, has the ability to decipher language, putting each word into its full context by analysing the words that come before and after it. Not only does this provide a greater understanding and insight into why a person is searching, it also allows for careful cherry-picking of individual passages and video segments that are most likely to answer the query – more on this in just a sec.
Google is also quick to point out that the change, like all other ranking factors, is applied fairly to all websites. The cynical amongst you may take that last part with a pinch of salt (literally as I write this I’m getting a Twitter notification to say the US DOJ is filing a monopoly lawsuit against Google) but whatever the motivation there are some very useful features coming into play. Let’s take a gander, shall we?
Spelling and Passages
BERT is essentially a neural network, which allows for greater data referencing thanks to its ability to be “trained”. As a result, BERT is able to consider the context of the entire search query instead of individual words, and can therefore bypass any spelling errors you make. One in ten queries are misspelled every day, so this will make a big difference. The “Did you mean” feature already handles a lot of these, but the new function calls on a staggering number of data parameters to establish a response despite spelling errors.
Thanks to its enhanced ability to understand context, BERT also has a better understanding of the nuances of specific webpages, and the answers held within.
Type in a question now and often you’ll be greeted with a mostly relevant answer directly quoted from a website. BERT is able to take this to a new level, indexing specific passages or sentences of a website to find the answer most relevant to the query.
The aim, it seems, is to expand on this to make the answers more specific to the search query rather than the occasions where Google will just recommend a website and leave you to the business of trawling through.
Let’s look at a quick example: Here the word “to” is important as it establishes the user wants to travel from Brazil to the USA. The previous algorithm cannot recognise this and provides a result of USA travel to Brazil (the wrong way round!). By contrast, BERT understands the nuance in the question and provides a much more relevant result.

Subtopics
Google’s search algorithm will now also be able to index individual passages of text within web pages, in order to locate more specific information. The AI uses subtopics to narrow down broad search terms and find the specific information you’re looking for. In Google’s example, say you were to search for “home exercise equipment”, BERT will incorporate relevant subtopics such as budget equipment, premium picks and small space ideas, returning with a much broader range of results. This particular feature will become fully functional by the end of the year.
Data Detail
Sometimes words aren’t what you’re looking for, and Google’s AI is now able to return with actual data based on the language processing we’ve already touched on. The idea is that if you wanted to know, for example, the population of Chicago, Google would return an actual valid data point instead of recommending a website, where it may well be buried in a mound of text.
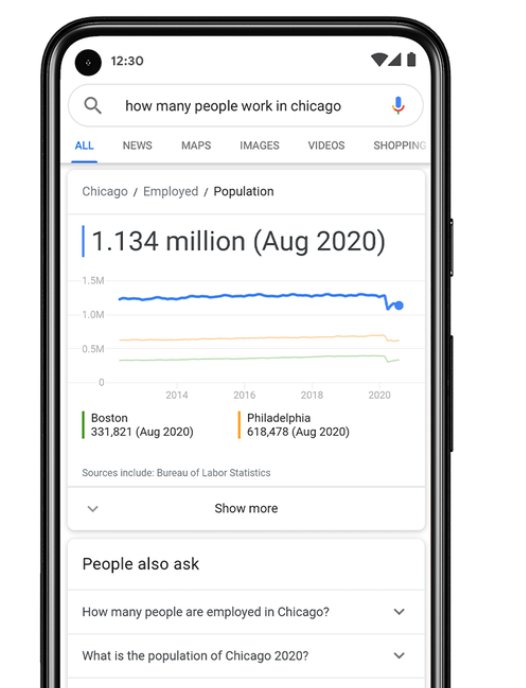
What makes this possible is the ongoing development of open statistical data networks such as The Data Commons Project. Google simply applies the algorithms discussed earlier to search the database and – presto!
COVID-19
Not exactly a header you’d want to see in any positive list, but hear us out. Google will also be able to show live traffic info as well as business COVID precautions, so shoppers can time their visits and take precautions accordingly. You can do this straight from the map too, so if you’re checking out a new cafe or heading to an unfamiliar store, you can know what to expect!
Videos
Google can now identify and tag important or informative key moments, which are bookmarked so they can be referred to when a user asks a related question. Want to see your favourite goal from the weekend, or find out how to change a plug without blowing yourself up? Well now you can get to the good stuff without sitting through the obligatory 10 minute introduction. Google anticipates that by the end of 2020, 10% of searches will incorporate this feature, so it’s one to keep on your radar!
Hum a Song
Hum a song and the Google assistant will find it for you. There isn’t much info on how well this works yet, so we can’t say whether it extends to Norwegian black metal or the back catalogue of Chas and Dave. We might experiment with this over the weekend and report back…
Other Cool Stuff
Google has also announced the launch of Pinpoint, as part of its Journalist Studio. Aimed at helping journalists, students and anyone who regularly faces hours of painstaking research, Pinpoint allows users to easily sift through and compile research from thousands of documents, videos etc. by zeroing in on specific names, organisations and locations.
For you visual learners and shopaholics out there, there are latest AR additions to Google Lens. Simply search what you see through your camera – Google now recognises over 15 billion different things and can help you to shop safely, translate languages and identify plants, animals and locations. You can learn more about Google Lens here: